Eymj.org
Yonsei Med J 53(4):842-848, 2012
pISSN: 0513-5796, eISSN: 1976-2437
Fluoxetine Protects against Big Endothelin-1 Induced
Anti-Apoptosis by Rescuing Kv1.5 Channels in Human
Pulmonary Arterial Smooth Muscle Cel s
FeiFeng Dai, ZhiFu Mao, Jun Xia, ShaoPing Zhu, and ZhiYong Wu
Department of Cardiothoracic Surgery, Renmin Hospital of Wuhan University, Wuhan, China.
Received: September 7, 2011
Purpose: Pulmonary Kv channels are thought to play a crucial role in the regulation
Revised: October 14, 2011
of cel proliferation and apoptosis. Previous studies have shown that fluoxetine up-
Accepted: October 24, 2011
regulated the expression of Kv1.5 and prevented pulmonary arterial hypertension in
Corresponding author: Dr. ZhiFu Mao,
monocrotaline-induced or hypoxia-induced rats and mice. The current study was de-
Department of Cardiothoracic Surgery,
signed to test how fluoxetine regulates Kv1.5 channels, subsequently promoting
Renmin Hospital of Wuhan University, 238 Jiefang Road, Wuchang District,
apoptosis in human PASMCs cultured
in vitro.
Materials and Methods: Human
Wuhan 430060, China.
PASMCs were incubated with low-serum DMEM, ET-1, and fluoxetine with and
Tel: 86-027-88041911-82230
without ET-1 separately for 72 h. Then the proliferation, apoptosis, and expression of
Fax: 86-027-88042292
TRPC1 and Kv1.5 were detected.
Results: In the ET-1 induced group, the upregula-
tion of TRPC1 and down regulation of Kv1.5 enhanced proliferation and anti-apop-
∙ The authors have no financial conflicts of
tosis, which was reversed when treated with fluoxetine. The decreased expression of
TRPC1 increased the expression of Kv1.5, subsequently inhibiting proliferation
while promoting apoptosis.
Conclusion: The results from the present study suggest-
ed that fluoxetine protects against big endothelin-1 induced anti-apoptosis and res-
cues Kv1.5 channels in human pulmonary arterial smooth muscle cel s, potential y
by decreasing intracel ular concentrations of Ca2+.
Key Words: Apoptosis, Kv1.5, human pulmonary arterial smooth muscle cel s
The development of pulmonary arterial hypertension (PAH) involves a complex constel ation of multiple genes and molecules, which interact with each other and subsequently activate intracel ular signaling pathways that eventual y result in pul-monary remodeling. Vascular remodeling has been confirmed to be a hal mark pathological feature of PAH, and is characterized by changes in the pulmonary vascular structures associated with medial hypertrophy, which are mainly caused
by an imbalance between the proliferation and apoptosis of pulmonary arterial
Yonsei University Col ege of Medicine 2012
smooth muscle cel s (PASMCs).
This is an Open Access article distributed under the
Pulmonary Kv channels are thought to play a crucial role in the regulation of cel
terms of the Creative Commons Attribution Non-
Commercial License (http://creativecommons.org/
proliferation and apoptosis. K+ fluxes have been implicated in both the early and
licenses/by-nc/3.0) which permits unrestricted non-
late stages of apoptosis, as the down regulation of Kv has been shown to induce in-
commercial use, distribution, and reproduction in any
medium, provided the original work is properly cited.
creases in intracel ular K+ concentrations ([K+]i) and tonical y inhibit caspase, fur-
Yonsei Med J http://www.eymj.org Volume 53 Number 4 July 2012
Fluoxetine Rescues Kv1.5
ther suppressing apoptosis. As shown in human and animal
ShangHai, China), and fluoxetine (F; Sigma-Aldrich, Shang-
models of PAH, resistance to apoptosis was further en-
Hai, China) with and without ET-1 separately for 72 hours.
hanced by the selective downregulation of Kv1.5 chan-nels.1-3 However, increases in Kv channel activity and ex-
MTT assay
pression have been widely associated with apoptotic
Cel proliferation was quantified by multiply-table tourna-
induction. And a previous study confirmed that the upregu-
ment (MTT) assay. Briefly, human PASMCs were plated
lation of Kv1.5 was correlated with an increase in apoptosis
into 96-wel microplates at the concentration of 2×103 cel s/
and inhibition of PAH.1,4
well and treated with the different drugs as described
Endothelin-1 (ET-1) has been implicated in the pathogen-
above. After incubation, 20 μL of the MTT reagent was
esis of pulmonary hypertension. And, there was clear evi-
added to each wel and the multiwel plates were incubated
dence of activation of the ET system in virtual y al pre-clin-
in a humidified atmosphere for 4 hours. Then, the superna-
ical models of PAH, as wel as in al categories of human
tant was removed from each wel and 200 μL/wel of di-
PAH.5 Its levels have been shown to be closely correlated
methyl sulfoxide (DMSO; Sigma-Aldrich, St. Louis, MO,
with the severity of pulmonary vascular remodeling.6 Inter-
USA) was added to solubilize the formed formazan salt
estingly, it was reported that extracellular application of
crystals. The solubilized formazan product was spectropho-
ET-1 significantly reduced the amplitude of currents gener-
tometrical y quantified at 570 nm using an ELISA reader
ated by K+ efflux through Kv1.5 channels. The inhibitory
(Biorad, Hercules, CA, USA). Data were expressed as a %
effect of ET-1 on Kv1.5 channels provided convincing evi-
of the control.
dence that the mitogenic effect of ET-1 may partial y result from its inhibition of Kv1.5 channels in human PASMCs.7
Reverse transcription-polymerase chain reaction
Fluoxetine, the highly selective 5-hydroxytryptamine
Total RNA was isolated from human PASMCs using TRIzol
transporter (5-HTT) inhibitor, was reported to confer partial
reagent (Sigma-Aldrich, St. Louis, MO, USA) according to
protection from PAH in chronical y hypoxic mice.8 Intrigu-
the manufacturer's instructions. The specific primers were
ingly, fluoxetine was recently reported to prevent and re-
designed from the coding regions of human Kv1.5 (forward
verse established PAH in monocrotaline (MCT)-induced
primer: 5'-TCCT CCG AGTCATCCG-3', reverse primer:
hypertensive rats.9-11 In addition, it was also reported that
5'-ACAGCGAGCCCACGATC-3'). As a control for the in-
the protective effect of fluoxetine against MCT-induced hy-
tegrity of RNA, the primers of glyceraldehydes phosphate
pertension was potential y by upregulating Kv1.5 channels
dehydrogenase (GAPDH) were used (forward primer: 5'-A
in rat. Therefore, the current study was designed to test the
GGTGAAGG TCGGAG TCAAC-3' and reverse primer:
hypothesis that the antiproliferative and protective effects
5'-CGCTCCTGGAAGATGG TGAT-3'). Amplified prod-
of fluoxetine are partial y due to the upregulation of Kv1.5
ucts were separated by 1.2% agarose gel electrophoresis
channels and subsequent promotion of apoptosis in human
and stained with ethidium bromide. PCR product bands
PASMCs cultured
in vitro.
were visualized by ultra violet light, and the intensity val-ues were measured by densitometric analysis with the Quantity One program (Bio-Rad) and normalized to the in-
MATERIALS AND METHODS
tensity values of GAPDH for quantitative comparisons.
The PCR product was sequenced and the amplified produc-
Cel preparation and culture
tion of human Kv1.5 and GAPDH were 306 and 232 bp,
Human PASMCs from normal subjects were purchased from
ATCC (Rockefel er, Mali organization, Manassas, VA, USA) and used at passages 6-8. PASMCs were cultured in Dulbec-
co's Modified Eagle Medium (DMEM) supplemented with
After 72 hours, cel s were harvested in cel lysis solution
10% fetal bovine serum (FBS), and maintained at 37°C in a
(BioDev-Tech. Company, Beijing, China); then protein was
humidified atmosphere of 5% CO2 in air. The growth of the
extracted. The resultant protein concentrations were deter-
cel s was arrested by replacing 10% FBS DMEM with FBS-
mined by BCA Protein Assay reagents (Beyotime Biotech-
free DMEM for 24 hours. The cel s were then incubated
nology, Jiangsu, China). The extracts were diluted in 5×
with low-serum DMEM (2% FBS), ET-1 (Enzo ALEXIS,
loading buffer and heated at 95°C for 5 minutes. Kv1.5 and
Yonsei Med J http://www.eymj.org Volume 53 Number 4 July 2012
FeiFeng Dai, et al.
TRPC1 proteins were detected using a standard Western blot
as 100%, and the results for the ET-1, F with or without ET-1
protocol. Briefly, 30 μg proteins were separated by 8% SDS
groups were expressed as a percentage of the value from the
PAGE at 100 V for 0.5 hour and 80 V for 1.5 hours, and then
Blank group.
transferred to a nitrocel ulose membrane (Mil ipore, Bil eri-ca, MA, USA) at 4°C, 200 mA for 1 hour by a Western blot
apparatus (Bio-Rad). The transferred membrane was blocked
Al samples were immunostained according to the protocol
with 10% skimmed milk for 1 hour at room temperature, and
of the Annexin V/PI apoptosis kit. The apoptosis ratio was
then the blocked membrane was incubated with a primary
analyzed using flow cytometry.
antibody against Kv1.5 (dilution 1 : 700; Santa Cruz Bio-technology, Santa Cruz, CA, USA), TRPC1 (dilution 1 : 400;
Santa Cruz Biotechnology) and GAPDH (dilution 1 : 700;
Al data are expressed as the mean±SEM. Al experiments
Santa Cruz Biotechnology) overnight at 4°C, respectively.
were performed at least with six independent Human PASMCs
After incubation with the horseradish peroxidase-conjugated
cultures. Statistical analyses were performed by one-way
secondary antibody (dilutions of 1 : 5000; Beijing Zhong
ANOVA.
p-values <0.05 were considered significant.
Shan-Golden Bridge Biological Technology Company, Bei-
jing, China) for 1 hour at room temperature, the immunoblot-
ting signals were visualized using a Western Luminescent Detection kit (Vigorous Biotechnology, Beijing, China). The
results were quantified by densitometry and the density of
Fluoxetine suppresses ET-1 induced human PASMCs
immunoblot ing was analyzed by scanning X-ray film with
Quantitative One software. The values of the relative density
Plasma and lung ET-1 expression were increased in PAH,
of the Kv1.5 and TRPC1 bands were normalized to the den-
and correlated with disease severity, including the degree of
sity of GAPDH to represent the amount of Kv1.5 and
PASMC proliferation.17 Fig. 1 shows the time course of hu-
TRPC1 protein. The ratio of the Blank group was regarded
man PASMC proliferation mediated by 2% FBS (Blank)
E (0.1) with F (1.0) (µM)
Fig. 1. Fluoxetine mediated anti-proliferation of human PASMCs against ET-1. (A) Time course of the 2% FBS (Blank) and ET-1 (0.01 to 1 μM) induced human
PASMCs proliferation (B). (C) The anti-proliferation of fluoxetine in a dose-dependent manner against ET-1 (0.1 μM). (D) The approximate proliferation be-
tween the 2% FBS and fluoxetine (1.0 μM) treated groups, induced by ET-1 (0.1 μM ). PASMCs, pulmonary arterial smooth muscle cel s; FBS, fetal bovine se-
rum; ET-1, endothelin-1; MTT, multiply-table tournament.
Yonsei Med J http://www.eymj.org Volume 53 Number 4 July 2012
Fluoxetine Rescues Kv1.5
(Fig. 1A) and ET-1 at concentrations of 0.01 to 1 μM (Fig.
1B). As shown in Fig. 1C, fluoxetine inhibited ET-1 (0.1 μM)-
mediated increase of human PASMC numbers at the concen-trations of 0.1 to 10 μM. Since the concentration of 1 μM fluoxetine suppressed proliferation approximately to that of
seen in 2% FBS (Blank), shown in Fig. 1D, this concentra-tion was used as the proper inhibitory dose. So, the final
concentrations of ET-1 and fluoxetine were set at 0.1 μM
and 1.0 μM, separately.
Fluoxetine suppresses ET-1 induced upregulation of
TRPC1 in human PASMCs
TRPC1 protein level 0.3
It has been reported that the activity and expression level of
TRPC1 protein is directly correlated to [Ca2+]i. In the present study, fluoxetine suppressed the expression of the TRPC1
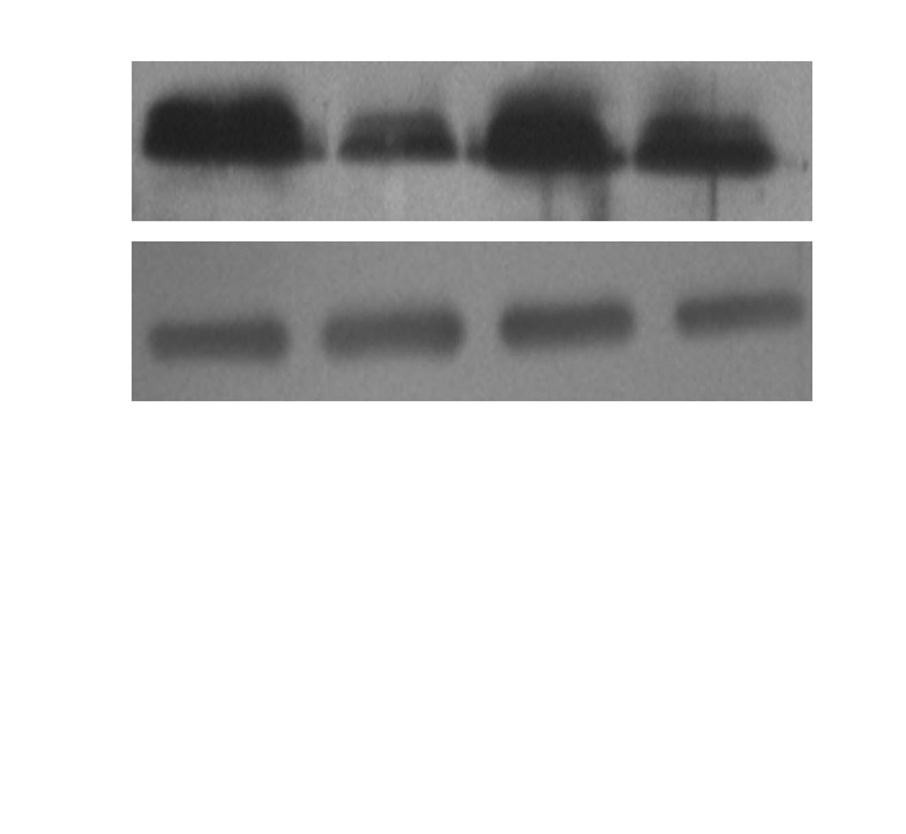
Fig. 2. Fluoxetine down regulated the expression of TRPC1 protein in ET-1
induced human PASMCs. Western blot results are displayed for TRPC1 (92
protein induced by ET-1. In Fig. 2, the expression of the
kDa) and GAPDH (34 kDa) in the human PASMCs cultured with low-serum
TRPC1 markedly increased in the ET-1 induced group com-
DMEM (2% FBS, Blank), ET-1, and fluoxetine with (ET-1+F) and without ET-1
(F) for 72 hours. Data, normalized to the amount of actin, are expressed as
pared with the Blank (1.2448±0.2157 vs. 0.6572±0.1076,
mean±SEM (n=7). *p<0.01 vs. Blank, †p<0.05 vs. ET-1. PASMCs, pulmonary
p<0.01). However, when treated with fluoxetine, it was down
arterial smooth muscle cel s; FBS, fetal bovine serum; TRPC, transient re-
ceptor potential channels; ET-1, endothelin-1; GAPDH, glyceraldehydes
regulated in the ET-1 induced group (0.7904±0.1043 vs.
phosphate dehydrogenase; SEM, standard error of mean.
1.2448±0.2157, p<0.05).
Fluoxetine upregulates the expression level of Kv1.5 in
ET-1 mediated human PASMCs
Pulmonary Kv1.5 channels are supposed to play a key role in
Kv1.5 protein level
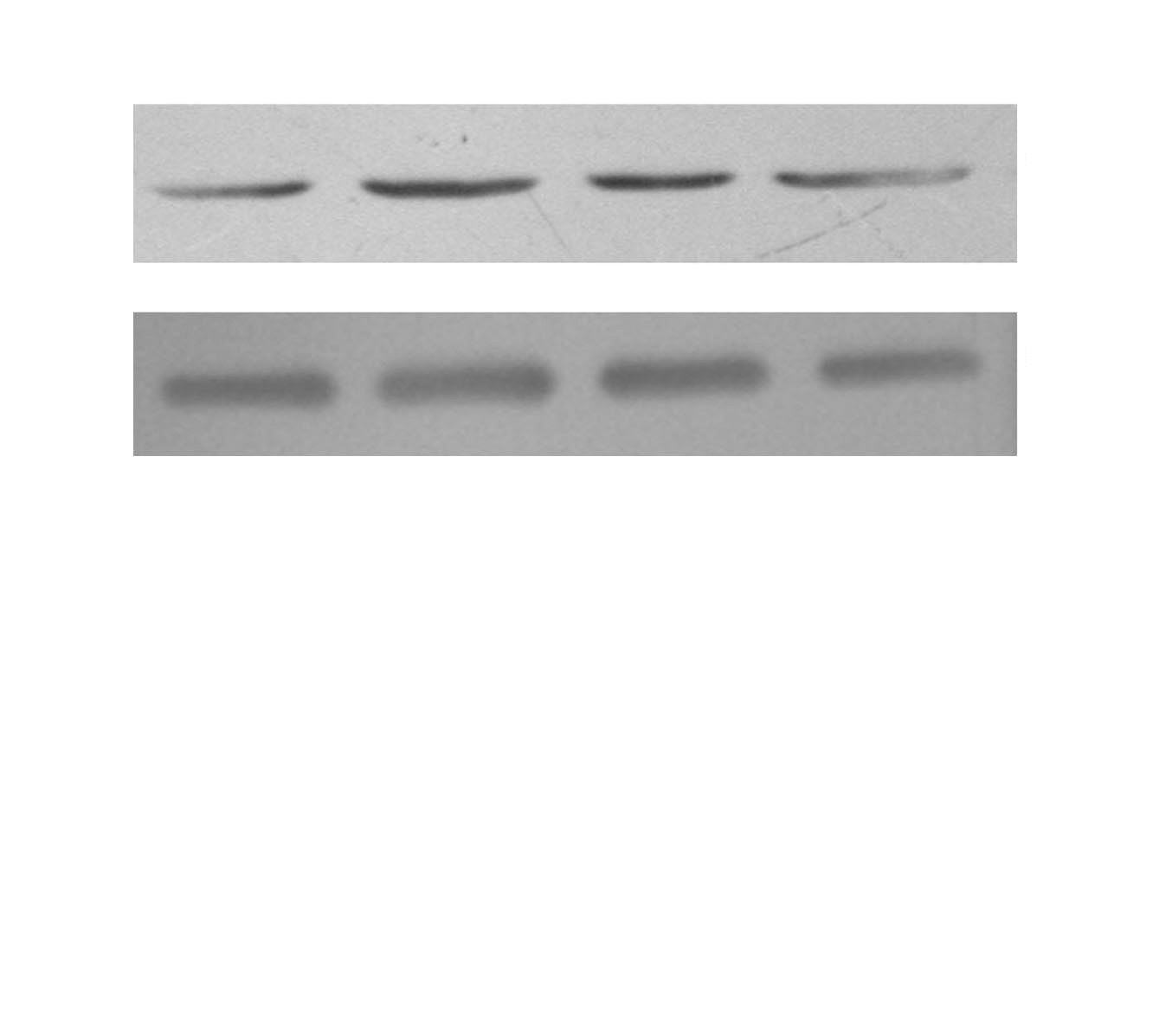
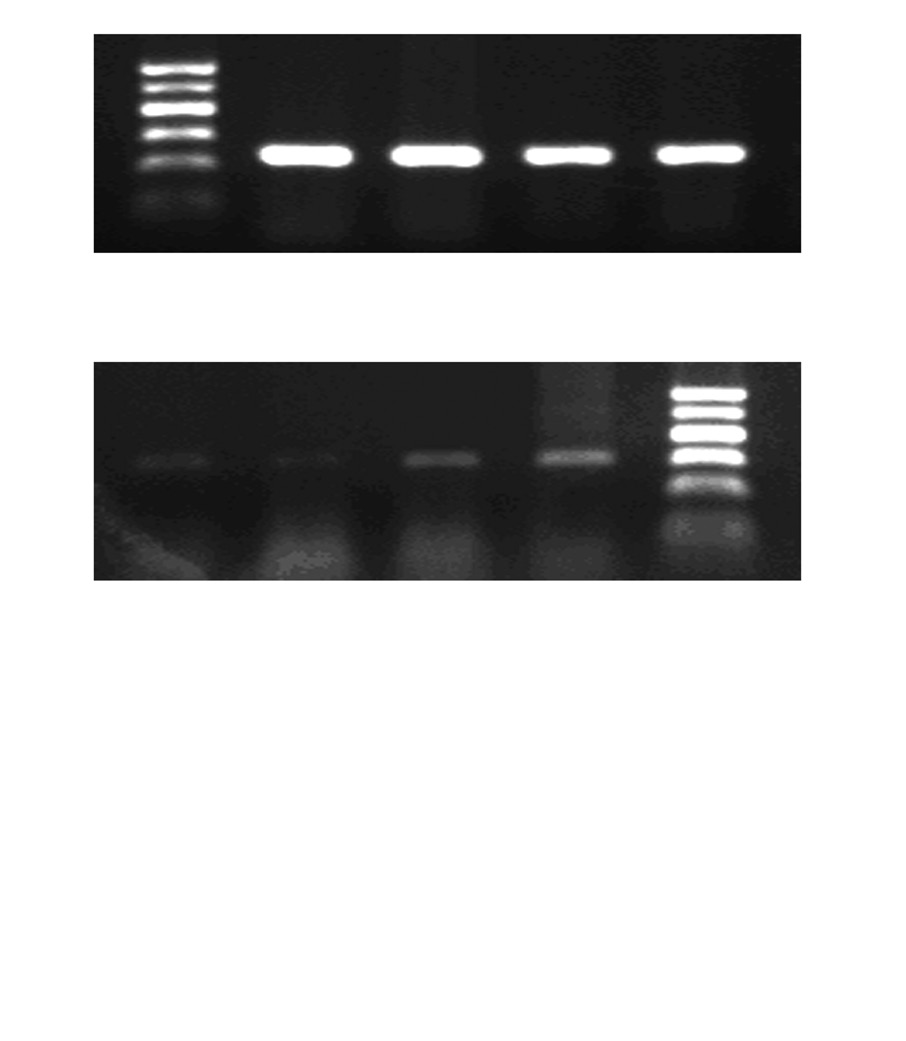
Fig. 3. Fluoxetine rescued the expression of Kv1.5 mRNA that was down
Fig. 4. Fluoxetine reversed the level of Kv1.5 protein in ET-1 induced human
regulated by ET-1 in human PASMCs. PCR amplified products are dis-
PASMCs. Western blot results are displayed for Kv1.5 (57-59 kDa) and
played for Kv1.5 (306 bp) and GAPDH (232 bp) in the human PASMCs cul-
GAPDH (34 kDa) in the human PASMCs cultured with low-serum DMEM
tured with low-serum DMEM (2% FBS, Blank), ET-1, and fluoxetine with
(2% FBS, Blank), ET-1, and fluoxetine with (ET-1+F) and without ET-1(F) for
(ET-1+F) and without ET-1(F) for 72 hours. Data, normalized to the amount of
72 h. Data, normalized to the amount of actin, are expressed as mean±SEM
GAPDH, are expressed as mean±SEM (n=7). *p<0.05 vs. Blank, †p<0.001 vs.
(n=9). *p<0.001 vs. Blank, †p<0.001 vs. ET-1. PASMCs, pulmonary arterial
ET-1, ‡p<0.001 vs. Blank. PASMCs, pulmonary arterial smooth muscle cel s;
smooth muscle cel s; FBS, fetal bovine serum; ET-1, endothelin-1; GAPDH,
ET-1, endothelin-1; GAPDH, glyceraldehydes phosphate dehydrogenase;
glyceraldehydes phosphate dehydrogenase; DMEM, dulbecco's modified
DMEM, dulbecco's modified eagle medium; SEM, standard error of mean;
eagle medium; SEM, standard error of mean.
PCR, polymerase chain reaction.
Yonsei Med J http://www.eymj.org Volume 53 Number 4 July 2012
FeiFeng Dai, et al.
Apoptosis ratio (%
Fig. 5. Fluoxetine enhanced the apoptosis ratio in ET-1induced human
Fig. 6. Fluoxetine enhanced the apoptosis ratio in ET-1induced human
PASMCs. The result from Flow Cytometry are displayed for the ratio of
PASMCs. The result from Flow Cytometry are displayed for the ratio of
apoptosis in the human PASMCs cultured with low-serum DMEM (2% FBS,
apoptosis in the human PASMCs cultured with low-serum DMEM (2% FBS,
Blank), ET-1, and fluoxetine with (ET-1+F) and without ET-1(F) for 72 h.
Blank), ET-1, and fluoxetine with (ET-1+F) and without ET-1(F) for 72 h. Data
PASMCs, pulmonary artery smooth muscle cel s; FBS, fetal bovine serum;
are expressed as mean±SEM (n=6). *p<0.01 vs. Blank, †p<0.001 vs. ET-1.
ET-1, endothelin-1; DMEM, dulbecco's modified eagle medium; PI,
PASMCs, pulmonary artery smooth muscle cel s; FBS, fetal bovine serum;
Propidium Iodide. FITC, fluoresceine isothiocyanate.
ET-1, endothelin-1; DMEM, dulbecco's modified eagle medium; SEM, stan-
dard error of mean.
the processes of proliferation and apoptosis. Results from
the fluoxetine treatment group in contrast with the ET-1 in-
semiquantitative RT-PCR analysis showed that the mRNA
duced group (4.85±0.3852 vs. 1.1±0.1634, p<0.001). Also,
expression of Kv1.5 in ET-1 induced human PASMCs was
there were no obvious changes between the Blank and fluox-
decreased remarkably, similar to the protein expression seen
etine only groups (2.2±0.1707 vs. 2.3834±0.0703, p>0.05).
with the Western blots. In Fig. 3, ET-1 significantly decreased the expression of Kv1.5 mRNA compared with the Blank
(0.0303±0.0034 vs. 0.0661±0.0051, p<0.05), as wel as the Kv1.5 protein (1.2198±0.1016 vs. 2.5717±0.1557, p<0.001), as seen in Fig. 4. Compared with the ET-1 induced group,
Pulmonary arterial hypertension is characterized by elevated
the same mRNA and protein were increased remarkably in
pulmonary vascular resistance, smooth muscle remodeling
the fluoxetine treatment group (0.1648±0.0087 vs. 0.0303±
and apoptosis, leading to right heart failure and death.4,12 Lu-
0.0034, p<0.001; 2.1234±0.1766 vs. 1.2198±0.1016, sepa-
men narrowing and medial hypertrophy of smal -sized pul-
rately, p<0.001). Although the Kv1.5 mRNA level was in-
monary arteries are hal marks of the pulmonary vascular re-
creased in the F group, compared with the Blank (0.1305±
modeling process, which are mainly due to an increased
0.01478 vs. 0.0661±0.0051, p<0.01), the expression of
number of pulmonary arterial smooth muscle cel s.13,14 The
Kv1.5 protein demonstrated no difference (2.5717±0.1557
imbalance between proliferation and apoptosis results in an
vs. 2.2290±0.0337, p>0.05).
augmentation on the number of PASMCs.4 Therefore, pre-cise control of the balance between PASMC proliferation and
Fluoxetine promotes the apoptosis ratio of ET-1
apoptosis is important to maintaining the structural and func-
induced human PASMCs
tional integrity of the pulmonary vasculature. Guignabert, et
The early stages of apoptosis in the human PASMCs treated
al.9 confirmed the efficacy of fluoxetine in preventing and re-
above were detected by Flow Cytometry. Compared with the
versing pulmonary vascular remodeling in rats, which made
Blank, as shown in Fig. 5 and Fig. 6, ET-1 induced apoptosis
fluoxetine a novel speculative therapeutic option for PAH.
inhibition was enhanced (1.1±0.1634 vs. 2.3834±0.0703,
The protection of fluoxetine against PAH in MCT-induced
p<0.01). Apparently, the apoptosis ratio was increased in
rats was also previously demonstrated.10,11 In the present
Yonsei Med J http://www.eymj.org Volume 53 Number 4 July 2012
Fluoxetine Rescues Kv1.5
study, fluoxetine suppressed proliferation and enhanced
stages was decreased, paral eling with the downregulation
apoptosis, reversing the imbalance between proliferation and
of Kv1.5 channels. Impressively, the human PASMCs treat-
apoptosis in human PASMCs induced by ET-1 in vitro.
ed with fluoxetine only changed in the mRNA expression
Pulmonary Kv channels are thought to play a crucial role
of Kv1.5, but no changes on the expression of protein was
in the maintenance of resting membrane potentials, and
observed, paralleling with the apoptosis ratio, compared
subsequently the vascular tone of pulmonary arteries. Alter-
ations in Kv channel function lead to several additional and
A detailed mechanism of the development of PAH is not
interrelated consequences, including the regulation of cel
yet known. The results from the present study showed that
proliferation and apoptosis, which ultimately leads to pul-
fluoxetine plays an important role in rescuing the expres-
monary vascular remodeling. It has been shown that dys-
sion of Kv1.5 channel in the ET-1 induced group. Potential-
function of Kv channels is closely linked to pulmonary vaso-
ly, the pharmacological blockade of 5-HTT may inhibit the
constriction and pulmonary vascular remodeling in PAH.9,15
activation of Ras/Rac system, down regulating the levels of
It was also becoming evident that proliferation of cultured
TRPC1 and [Ca2+]i and rescue Kv1.5 channels.
human PASMCs was associated with membrane depolar-
In conclusion, fluoxetine plays an important role in im-
ization and down regulation of Kv currents.16 As shown in
proving pulmonary vascular remodeling, by suppressing pro-
human and animal models of PAH, resistance to apoptosis
liferation, rescuing Kv1.5 channels and promoting apoptosis.
was further enhanced by the selective down regulation of Kv1.5 channels.1-3 A similar phenomenon was also observed
in persistent pulmonary hypertension of newborns.17 How-ever, increases in Kv channel activity and expression has
1. Bonnet S, Rochefort G, Sutendra G, Archer SL, Haromy A, Web-
been widely associated with apoptotic induction. And a pre-
ster L, et al. The nuclear factor of activated T cel s in pulmonary
vious study confirmed that the up regulation of Kv1.5 was
arterial hypertension can be therapeutically targeted. Proc Natl
correlated with an increase in the apoptosis/ proliferation
Acad Sci U S A 2007;104:11418-23.
ratio and inhibition of PAH.1,4 The available evidence pre-
2. Remil ard CV, Tigno DD, Platoshyn O, Burg ED, Brevnova EE,
Conger D, et al. Function of Kv1.5 channels and genetic varia-
sented to this point was quite strong regarding the role of
tions of KCNA5 in patients with idiopathic pulmonary arterial hy-
Kv channels in vascular smooth muscle cel apoptosis. Con-
pertension. Am J Physiol Cel Physiol 2007;292:C1837-53.
versely, there was also mounting evidence that Kv channel
3. Bonnet S, Michelakis ED, Porter CJ, Andrade-Navarro MA,
Thébaud B, Bonnet S, et al. An abnormal mitochondrial-hypoxia
activation may also play a significant role in promoting
inducible factor-1alpha-Kv channel pathway disrupts oxygen
proliferation.18
sensing and triggers pulmonary arterial hypertension in fawn
In the present study, the expression of the TRPC1 mark-
hooded rats: similarities to human pulmonary arterial hyperten-
edly increased in the ET-1 induced group compared with
sion. Circulation 2006;113:2630-41.
4. McMurtry MS, Bonnet S, Wu X, Dyck JR, Haromy A, Hashimoto
the Blank, and the expressions of Kv1.5 were decreased
K, et al. Dichloroacetate prevents and reverses pulmonary hyper-
both in the levels of transcription and translation. Previous-
tension by inducing pulmonary artery smooth muscle cel apopto-
ly, reports demonstrated that [Ca2+]i inhibited K+ channels
sis. Circ Res 2004;95:830-40.
5. Michel RP, Langleben D, Dupuis J. The endothelin system in pul-
in canine pulmonary arteries,19 and it had also been reported
monary hypertension. Can J Physiol Pharmacol 2003;81:542-54.
that ET-1 induced-increases of [Ca2+]i were mainly caused
6. Rubens C, Ewert R, Halank M, Wensel R, Orzechowski HD,
by its upregulation of transient receptor potential channels
Schultheiss HP, et al. Big endothelin-1 and endothelin-1 plasma
(TRPC), especial y TRPC1.20 And, when treated with fluox-
levels are correlated with the severity of primary pulmonary hy-
pertension. Chest 2001;120:1562-9.
etine, it was found that fluoxetine down regulated TRPC1
7. Shimoda LA, Sylvester JT, Booth GM, Shimoda TH, Meeker S,
and rescued ET-1 induced Kv1.5 down-regulation in the
Undem BJ, et al. Inhibition of voltage-gated K(+) currents by en-
levels of transcription and translation and promoted apopto-
dothelin-1 in human pulmonary arterial myocytes. Am J Physiol
Lung Cel Mol Physiol 2001;281:L1115-22.
sis in human PASMCs in vitro. The results from the present
8. Marcos E, Adnot S, Pham MH, Nosjean A, Raffestin B, Hamon
study demonstrated that the upregulation of TRPC1 down
M, et al. Serotonin transporter inhibitors protect against hypoxic
regulated the expression of Kv1.5 protein and mRNA in
pulmonary hypertension. Am J Respir Crit Care Med 2003;168:
human PASMCs induced by ET-1, potential y by regulating
9. Guignabert C, Raffestin B, Benferhat R, Raoul W, Zadigue P,
the intracellular concentrations of Ca2+ in vitro. Further-
Rideau D, et al. Serotonin transporter inhibition prevents and re-
more, compared with the Blank, the apoptosis ratio of early
verses monocrotaline-induced pulmonary hypertension in rats.
Yonsei Med J http://www.eymj.org Volume 53 Number 4 July 2012
FeiFeng Dai, et al.
ulation of pulmonary artery smooth muscle cel proliferation and
10. Zhu SP, Mao ZF, Huang J, Wang JY. Continuous fluoxetine ad-
apoptosis: pharmacotherapeutic implications. Br J Pharmacol
ministration prevents recurrence of pulmonary arterial hyperten-
2008;153 Suppl 1:S99-111.
sion and prolongs survival in rats. Clin Exp Pharmacol Physiol
16. Platoshyn O, Golovina VA, Bailey CL, Limsuwan A, Krick S, Ju-
haszova M, et al. Sustained membrane depolarization and pulmo-
11. Zhai FG, Zhang XH, Wang HL. Fluoxetine protects against
nary artery smooth muscle cel proliferation. Am J Physiol Cel
monocrotaline-induced pulmonary arterial hypertension: potential
roles of induction of apoptosis and upregulation of Kv1.5 chan-
17. Konduri GG, Bakhutashvili I, Eis A, Gauthier KM. Impaired volt-
nels in rats. Clin Exp Pharmacol Physiol 2009;36:850-6.
age gated potassium channel responses in a fetal lamb model of
12. Farber HW, Loscalzo J. Pulmonary arterial hypertension. N Engl J
persistent pulmonary hypertension of the newborn. Pediatr Res
13. Fantozzi I, Platoshyn O, Wong AH, Zhang S, Remillard CV,
18. Neylon CB. Potassium channels and vascular proliferation. Vascul
Furtado MR, et al. Bone morphogenetic protein-2 upregulates ex-
pression and function of voltage-gated K+ channels in human pul-
19. Post JM, Gelband CH, Hume JR. [Ca2+]i inhibition of K+ chan-
monary artery smooth muscle cel s. Am J Physiol Lung Cel Mol
nels in canine pulmonary artery. Novel mechanism for hypoxia-
induced membrane depolarization. Circ Res 1995;77:131-9.
14. Krick S, Platoshyn O, McDaniel SS, Rubin LJ, Yuan JX. Aug-
20. Wang C, Wang J, Zhao L, Wang Y, Liu J, Shi L, et al. Sildenafil
mented K(+) currents and mitochondrial membrane depolarization
inhibits human pulmonary artery smooth muscle cel proliferation
in pulmonary artery myocyte apoptosis. Am J Physiol Lung Cel
by decreasing capacitative Ca2+ entry. J Pharmacol Sci 2008;108:
Mol Physiol 2001;281:L887-94.
15. Burg ED, Remil ard CV, Yuan JX. Potassium channels in the reg-
Yonsei Med J http://www.eymj.org Volume 53 Number 4 July 2012
Source: http://www.eymj.org/Synapse/Data/PDFData/0069YMJ/ymj-53-842.pdf
Tamoxifen for Prevention of Breast Cancer:Report of the National Surgical Adjuvant Breast andBowel Project P-1 Study Bernard Fisher, Joseph P. Costantino, D. Lawrence Wickerham, Carol K.Redmond, Maureen Kavanah, Walter M. Cronin, Victor Vogel, Andre´Robidoux, Nikolay Dimitrov, James Atkins, Mary Daly, Samuel Wieand,Elizabeth Tan-Chiu, Leslie Ford, Norman Wolmark, and other NationalSurgical Adjuvant Breast and Bowel Project Investigators
eNeonatal Review VOLUME 10, ISSUE 7 TREATMENT STRATEGIES FOR GERD IN NEONATES In this Issue. Length of Activity Gastroesophageal reflux (GER), the passage of gastric contents into the esophagus, is 1.0 hour Physicians common in neonates and infants. Regurgitation with clinical y significant sequelae 1.0 contact hour Nurses




