Cjns.gums.ac.ir
Caspian Journal of Neurological Sciences
http://cjns.gums.ac.ir
BDNF Pretreatment Attenuates Morphine-Induced Learning
and Memory Impairment in Rats
Babaei Parvin (PhD) 1,2* , Vahdati Sanaz (MD Stu) 2 , Soltani-Tehrani Bahram (PhD) 1
A B S T R A C T
Article type:
Background: It has been known that Brain-Derived Neurotrophic Factor
Original Article
(BDNF) is involved in neural survival and long term memory (LTM). Here we
hypothesized that BDNF as a potent neurotrophic factor might modulate
amnestic effect induced by morphine.
Objectives: The aim of this study was to examine whether infusion of
Article history:
exogenous BDNF in the CA1 regions of the dorsal hippocampi could ameliorate
Received: 19 January 2014 Accepted: 23 May 2014
memory impairment induced by morphine.
Available online: 20 March 2015
Materials and Methods: Forty rats were divided into 5 groups for dose
CJNS 2015; 1 (1): 12-18
response study of morphine (2.5, 5, 7.5 and 10 mg/kg morphine, and saline,
intraperitoneal) on memory retention. For second part of the experiment 24
animals were divided into three groups: (morphine +BDNF, morphine + saline
and saline + saline). Two weeks after stereotaxic surgery, animals received 0.5
μl bilateral infusion of either saline or BDNF (5 µg/rat) intrahippocampally, 30
1. Cellular & Molecular Research Center,
Faculty of Medicine, Guilan University
minutes before morphine treatment (7.5 mg/kg, i.p.). Step-through inhibitory
of Medical Sciences, Rasht, Iran
avoidance task has been used to examine retrieval of memory formation, 1.5
and 24 h after the training.
2. Physiology Department, Faculty of
Medicine, Guilan University of Medical
Results: The results showed that systemic administration of 7.5 and 10 mg/kg
Sciences, Rasht, Iran
morphine compared with saline immediately after the training impairs long-
term retention of memory for passive avoidance task in rats tested 24 hours
later (
p < 0.01). Surprisingly intra-CA1 microinjection of BDNF 30 minutes
prior to injection of morphine significantly prevented amnesia (
p < 0.001).
Conclusions: These findings suggested that increase the level of BDNF in the
CA1 region of the hippocampus during 30 minutes time window before
morphine administration might modulate morphine-induced amnesia.
Keywords: Brain-Derived Neurotrophic Factor; Amnesia; Morphine; Rats
*Corresponding author:
Physiology Department, Faculty of
Copyright 2015 Caspian Journal of Neurological Sciences. All rights reserved.
Medicine, Guilan University of
Medical Sciences, Rasht, Iran
Please cite this paper as:
Email:
[email protected]
Babaei P, Vahdati S, Soltani-Tehrani B. BDNF Pretreatment Attenuates Morphine-Induced Learning and Memory Impairment in Rats. Caspian J Neurol Sci 2015; 1(1):12-18.
Introduction
orphine has been widely used in
influence on the processes of learning and
pain treatment, but its strong
causes memory impairment. Impairment of
M dependency potential is a serious memory has been reported after both chronic
challenge to its clinical usage. It is reported
and acute morphine administration (1-4). Pre-
that opioid peptides, especially morphine
or post-training administration of morphine
BDNF and Morphine -Induced Amnesia Babaei P et al.
impairs specifically performance in the
xylazine (100 and 10 mg/kg, respectively),
passive avoidance task (3, 5).
and fixed in the flat –skull position using
Memory is critically depended on the
hippocampus region, and can be divided into
Instruments, USA).The rats' scalp were cut, a
short-term and long-term forms (6, 7).
small craniotomy was drilled and cannulas
Consolidation of short term (STM) to long-
term (LTM) memory takes place immediately
implanted into the CA1 region of the
following the training experience (8, 9). This
hippocampus at coordinates: AP − 3mm, L ±
critical period is influenced by different
2mm and V − 2.8mm (19).
neurotransmitters
Micro infusions:
Moreover, LTM strongly depends on protein
Morphine sulphate (Darupakhsh, Iran) and
synthesis cascades and neurotropic factors
human recombinant BDNF (R&D, USA) were
particularly BDNF (14-16). According to the
dissolved in sterile 0.9% saline. First, animals
previous reports hippocampal BDNF appears
were divided into five groups (saline,
to be necessary for LTM formation in the
morphine 2.5, 5, 7.5 and 10 mg/kg.) for dose
different discrete periods, immediately after,
response study of morphine. Secondly, 24 rats
1.4 hour and 3.6 hours after training (17, 18).
were divided into three experimental groups
Although many studies proposed that BDNF is
(morphine + BDNF, morphine + saline and
a key molecule mediating persistence and
saline + saline, n = 8 each) and underwent
maintenance LTM, it is still unclear whether
stereotaxic surgery. Two weeks later, animals received a 0.5 μl bilateral infusion of saline or
BDNF pretreatment is capable of ameliorating memory
(2.5µg/0.5μl/side)
conducted to answer to this question.
hippocampally 30 minutes before morphine
treatment (7.5 mg/kg, i.p.).
Materials and Methods
Inhibitory avoidance apparatus:
The apparatus consisted of two equal size of
Sixty four male wistar rats weighing 200-
compartments, one light and one dark
250g were used in this study. They had free
(20×20×30 cm high), connecting via a
access to food and water, and kept at 24 ± 2 C
guillotine door (7×9 cm). The floor of the dark
under a 12h/12h light dark cycle. Each group
compartment was made of stainless steel rods
consisted of 8 animals and each animal was
(2.5 mm in diameter) with a distance of 1 cm.
tested once. All experiments were conducted
For the acquisition trial, rat was placed in the
in accordance with the Guide for Care and Use
light compartment and the door between the
of Laboratory Animals (National Institute of
two compartments was opened 20 seconds
Health Publication No.80-23, revised 1996)
later. When the rat entered the dark
approved by the Research and Ethics
compartment, the door closed and an electric
Committee of Guilan University of Medical
foot shock (1 mA, 50 Hz, 5 seconds) was
Sciences.
delivered through the grid floor. For the
retention trial, the rat was again placed in the
light compartment 1.5 and 24 hours following
The animals were anaesthetized via the
the acquisition trial. The latency time
intraperitoneal (i.p.) injection of ketamine and
Caspian J Neurol Sci 2015 March; 1(1): 12-18
(seconds) for entering the dark compartment
Upon completion of the inhibitory avoidance
test, each rat was deeply anesthetized and 1 ml
of a 4% methylene-blue solution was
bilaterally infused through the cannula into the
decapitated and the brains were removed and placed in formaldehyde for two days (10%).
Diagram 1. The effect of post-training administration of morphine on
step-through latency. The rats (n = 8 per group) received post-training
Then, the brains were sliced and the injection
saline (1 ml/kg, i.p.) or varying doses of morphine (mor) (2.5, 5, 7.5 and 10 mg/kg, i.p.) and were tested after 1.5 h and 24 h. **p < 0.01
site was verified according to the Paxinos
compared with the saline.
&Watson, brain atlas 2005(19), (Figure1).
Following infusion of BDNF or saline, a 30
minutes wait-time and then an i.p. injection of morphine or saline, the rats performed the acquisition trial of the inhibitory avoidance test. Memory was assessed during the retention trial by measuring step-through latency in the passive avoidance task observed 1.5 and 24 hours after the acquisition trial
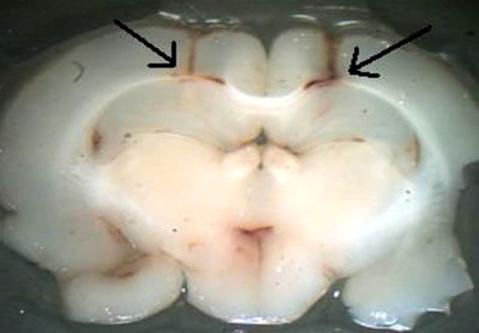
Figure 1. Photomicrograph from rat brain section showing the
extension of the area reached by infusions into the hippocampus.
Data analysis:
Each value represents the mean ± standard
error of the mean (S.E.M.). After assaying the
normality of data with Kolmogorov - Smirnov test, comparison of data among groups was
BDNF + mor (1.5h)
BDNF + mor (24h)
performed using one-way analysis of variance
Diagram 2. The effect of acute BDNF pretreatment on memory
with Tukey's post-test , when the p-values was
consolidation prior to morphine injection. The latencies for the rat (n = 8 per group) to enter to the dark room 1.5 h and 24 h after the
< 0.05, the difference was considered to be
training were expressed as mean ± S.E.M. *p < 0.01 , ***p < 0.001
significant. Calculations were performed using
compared to morphine.
the SPSS statistical package version 19.
There was a strong significant group effect
(F(2, 21) = 37; p = 0.001, one way ANOVA)
showing that the group receiving BDNF 30
During the training trial, there was no
minutes prior to morphine administration
significant difference among groups (p > 0.05,
(BDNF + morphine) took longer to enter the
one way ANOVA). Systemic post-training
dark chamber compared to either control
administration of morphine (7.5 and 10
group, saline + morphine or saline + saline.
significantly decreased latency to enter to the
dark compartment compared to the control
receiving saline (p < 0.01; Diagram 1).
BDNF and Morphine -Induced Amnesia Babaei P et al.
Discussion
memory by promoting neural plasticity (29,
30). Additionally, BDNF is required for the
In the current study, we showed that
consolidation of short-term and long-term
administration of morphine immediately after
memory, especially in glutamatergic and
training impairs memory retention in the
GABAergic synapses (29, 31-33). Previous
studies report an increase in BDNF mRNA in
the dentate gyrus of the hippocampus
hippocampal CA1 region, 30 minutes before
following the acquisition trial (17, 34).
morphine administration, ameliorated the
Conversely, Alonso et al. (2002) showed that
morphine-induced memory impairment.
infusion of an anti-BDNF antibody impaired
The impairment of memory induced by
LTM, when given 15 minutes before or 1 and
morphine is consistent with previous studies
4 hours after training (17). Our results were in
(3, 20, 21). Based on the immediate post-
agreement with the Johnston et al. study
training administration of morphine and its
showing that injection of recombinant BDNF
short half-life in the brain (approximately 1
before training enhanced memory recall in day
hour), it is likely that morphine is affecting the
old chicks (35). Our findings confirmed that
early phase of memory consolidation (22).
30 minutes before the induction of amnesia
Opioids produce their principal effects on
was a sensitive time window which was
memory by binding to at least three different types of receptors: μ, δ and κ opioid receptors
critical for LTM formation, so it is more likely to relate this result to acute effects of BDNF
(3). All opioid receptor subtypes inhibit
on synaptic transmission, rather than protein
adenylyl cyclase and Ca2+ channels and
synthesis due to inadequate time. Binding of
stimulate K+ channels. These effects are
BDNF to tropomyosin receptor kinase B
required for morphine-induced amnesia in the
(TrkB) triggers a number of intra-cellular
passive avoidance test (23). Alternately,
signalling pathways from long lasting effects
neuropharmacological studies have revealed
to enhancing early long term potentiation
that activation of opioid receptors may
(LTP) and phosphorylation of synaptic
decrease the function of the cholinergic
proteins (36-39). Rapid Ca2+ influx through
system (24-26). However, one cannot exclude
the possibility that morphine interferes with
subsequent protein phosphorylation events
other neurotransmitter systems, such as
modify pre-existing synapses and trigger early
adrenergic or dopaminergic, to induce amnesia
LTP, an important mechanism mediating
memory formation (40, 41). A recent
Interestingly, we also showed that infusion of
surprising study revealed suppressive effect of
BDNF into the dorsal hippocampus 30
BDNF as a negative modulator on morphine
minutes before training was sufficient to
reward (42). Some of the neurotransmitters
prevent the amnestic effect of morphine as
regulate BDNF synthesis, and in turn they are
well as enhance memory consolidation
regulated by BDNF. For example BDNF
compared to the saline control group. To our
knowledge, this study was the first to
glutamate release in the hippocampus,
demonstrate that BDNF attenuates morphine-
depolarizes neurons and interferes in Ca
induced memory impairment.
signaling (43-51). The significance of these
Animal and human studies suggest that
reciprocal regulations was intriguing and
hippocampal BDNF plays a major role in
Caspian J Neurol Sci 2015 March; 1(1): 12-18
could represent a novel framework into the
6. Milner B, Squire LR, Kandel ER. Cognitive
molecular basis of morphine–induced amnesia.
Neuroscience Review and the Study of Memory. Neuron 1998; 20:445-68.
For future studies we propose administration
7. Kumaran D, Maguire EA. The Human
of antibody against BDNF and also different
Hippocampus: Cognitive Maps or Relational
doses of BDNF prior to morphine injection.
Memory?. J Neurosci 2005; 25(31):7254-9.
8. Bekinschtein P, Cammarota M, Igaz LM,
Conclusion
Persistence of Long-Term Memory Storage
The present study shows that morphine
Requires a Late Protein Synthesis-and BDNF-
impairs the consolidation phase of long-term
dependent Phase in the Hippocampus. Neuron
recognition memory, possibly by preventing a
2007; 53(2):261-77.
9. Castellano C, Cestari V, Ciamei A. NMDA
learning-induced increase in BDNF levels in
the hippocampus. This study suggests that
Processes. Curr Drug Targets 2001; 2(3):273-
intra-hippocampal
prevents the deficit in memory consolidation
10. Camera K, Mello C, Ceretta A, Rubin MA.
caused by morphine.
Systemic Administration of Polyaminergic Agents Modulate Fear Conditioning in Rats.
Psychopharmacology 2007; 192(4):457-64.
Conflict of Interest
11. Cammarota M, Bevilaqua LR, Rossato JI,
Lima RH, Medina JH, Izquierdo I. Parallel
No conflict of interest.
Memory Processing by the CA1 Region of the Dorsal Hippocampus and the Basolateral
References
Amygdala. Proc Natl Acad Sci U S A 2008;
105(30):10279-84.
1. Ma M, Chen Y, He J, Zeng T, Wang JH.
12. Decker MW, McGaugh JL. The Role of
Effects of Morphine and Its Withdrawal on Y-
Interactions between the Cholinergic System
Maze Spatial Recognition Memory in Mice.
and Other Neuromodulatory Systems in
Neuroscience 2007; 147(4):1059-65.
Learing and Memory. Synapse 1991; 7(2):151-
2. Castellano C, Pavone F, Allegra S. Morphine
and Memory in DBA/2 Mice: Effects of Stress
and of Prior Experience. Behav Brain Res
Requirement of Dopamine Signaling in the
1984; 11(1):3-10.
Amygdala and Striatum for Learning and
3. Itoh S, Takashima A, Igano K, Inouye K.
Maintenance of a Conditioned Avoidance
Memory Effect of Caerulein and Its Analogs in
Response. Learn Mem 2011; 18(3):136-43.
Active and Passive Avoidance Responses in
14. Rossato J, Bevilaqua L, Izquierdo I, Medina
the Rat. Peptides 1989; 10(4):843-8.
4. Izquierdo I, Bevilaqua LM, Rossato JI, da
Persistence of Long-Term Memory Storage.
Silva WC, Bonini J, Medina JH, et al. The
Science 2009; 325(5943):1017-20.
15. Slipczuk L, Bekinschtein P, Katche C,
Potentiation Underlie Memory Consolidation
Cammarota M, Izquierdo I, Medina JH. BDNF
of One-Trial Avoidance in the CA1 Region of
the Dorsal Hippocampus, But Not in the
Expression Required for Memory Formation.
Basolateral Amygdala or the Neocortex.
PLoS One 2009; 4(6):e6007.
Neurotox Res 2008; 14(2-3):273-94.
16. Schinder AF, Poo M-m. The Neurotrophin
5. Khavandgar S, Homayoun H, Zarrindast MR.
Hypothesis for Synaptic Plasticity. Trends
The Effect of L-NAME and L-arginine on
Neurosci 2000; 23(12):639-44.
Impairment of Memory Formation and State-
17. Alonso M, Vianna MR, Depino AM, Mello e
Dependent Learning Induced by Morphine in
Souza T, Pereira P, Szapiro G, et al. BDNF–
Mice. Psychopharmacology 2003; 167(3):291-
triggered Events in the Rat Hippocampus Are
Required for Both Short‐and Long‐Term
BDNF and Morphine -Induced Amnesia Babaei P et al.
Memory Formation. Hippocampus 2002;
28. Zarrindast MR, Farahmandfar M, Rostami P,
Rezayof A. The Influence of Central
18. Igaz L, Vianna M, Medina J, Izquierdo I. Two
Cholinergic Agents on Morphine-Induced
Amnesia in Morphine-Sensitized Mice. J
Consolidation of Fear-Motivated Learning. J
Psychopharmacol 2006; 20(1):59-66.
Neurosci 2002; 22(15):6781-9.
29. Poo M. Neurotrophins as Synaptic Modulators.
19. Paxinos G, Watson C. The Rat Brain in
Nat Rev Neurosci 2001; 2(1):24-32.
Stereotaxic Coordinates. 5th ed. San Diego:
30. Lu Y, Christian K, Lu B. BDNF: A Key
Academic Press; 2004.
Regulator for Protein Synthesis-Dependent
20. Pavone F, Castellano C. Effects of Tifluadom
LTP and Long-Term Memory?. Neurobiol
on Passive Avoidance Behaviour in DBA/2
Learn Mem 2008; 89(3):312-23.
mice. Behav Brain Res 1985;15(3):177-81.
31. Tyler WJ, Alonso M, Bramham C, Pozzo-
21. Zarrindast MR, Asadi F, Rezayof A. Repeated
Miller LD. From Acquisition to Consolidation:
Pretreatment of Morphine Prevents Morphine-
on the Role of Brain-Derived Neurotrophic
Induced Amnesia: A Possible Involvement for
Factor Signaling in Hippocampal-Dependent
Dorsal Hippocampal NMDA Receptors. Arch
Learning. Learn Mem 2002; 9(5):224-37.
Iran Med 2011; 14(1):32-8.
32. Rutherford L, Nelson S, Turrigiano G. BDNF
22. Bouw M, Xie R, Tunblad K, Hammarlund-
Has Opposite Effects on the Quantal
Udenaes M. Blood‐Brain Barrier Transport and
Brain Distribution of Morphine‐6‐Glucuronide
Interneuron Excitatory Synapses. Neuron
in Relation to the Antinociceptive Effect in
1998; 21(3):521-30.
33. Vicario-Abejón C, Collin C, McKay R, Segal
Modelling. Br J Pharmacol 2001; 134(8):1796-
M. Neurotrophins Induce Formation of
Functional Excitatory and Inhibitory Synapses
23. Galeotti N, Ghelardini C, Bartolini A.
between Cultured Hippocampal Neurons. J
Differential Prevention of Morphine Amnesia
Neurosci 1998; 18(18):7256-71.
by Antisense Oligodeoxynucleotides Directed
34. Falkenberg T, Mohammed A, Henriksson B,
Against Various Gi‐protein α Subunits. Br J
Persson H, Winblad B, Lindefors N. Increased
Pharmacol 2001; 133(2):267-74.
Expression of Brain-Derived Neurotrophic
24. Ukai M, Lin H. Involvement of μ Opioid
Factor mRNA in Rat Hippocampus Is
Receptors and Cholinergic Neurotransmission
Associated with Improved Spatial Memory and
in the Endomorphins-Induced Impairment of
Enriched Environment. Neurosci Lett 1992;
Passive Avoidance Learning in Mice. Behav
Brain Res 2002; 129(1):197-201.
35. Johnston A, Rose S. Memory Consolidation in
25. Li Z, Wu C, Pei G, Xu NJ. Reversal of
Day-Old Chicks Requires BDNF but Not NGF
Morphine-Induced Memory Impairment in
or NT-3; an Antisense Study. Brain Res Mol
Mice by Withdrawal in Morris Water Maze:
Brain Res 2001; 88(1):26-36.
Possible Involvement of Cholinergic System.
36. Yoshii A, Paton M. Postsynaptic BDNF‐TrkB
Pharmacol Biochem Behav 2001; 68(3):507-
Signaling in Synapse Maturation, Plasticity,
and Disease. Dev Neurobiol 2010; 70(5):304-
26. Baratti C, Introini I, Huygens P. Possible
37. Alder J, Thakker-Varia S, Bangasser D,
Muscarinic and Opioid Peptidergic Systems
Kuroiwa M, Plummer MR, Shors TJ, et al.
during Memory Consolidation in Mice. Behav
Brain-Derived Neurotrophic Factor-Induced
Neural Biol 1984; 40(2):155-69.
Gene Expression Reveals Novel Actions of
27. Homayoun H, Moghaddam B. NMDA
VGF in Hippocampal Synaptic Plasticity. J
Receptor Hypofunction Produces Opposite
Neurosci 2003; 23(34):10800-8.
Effects on Prefrontal Cortex Interneurons and
38. Almeida R, Manadas B, Melo C, Gomes
27(43):11496-500.
Neuroprotection by BDNF Against Glutamate-Induced Apoptotic Cell Death Is Mediated by
Caspian J Neurol Sci 2015 March; 1(1): 12-18
ERK and PI3-kinase Pathways. Cell Death
Neurotransmitter Release Induced by Brain-
Differ 2005; 12(10):1329-43.
Derived Neurotrophic Factor in Cultured
39. Jovanovic J, Thomas P, Kittler J, Smart
Hippocampal Neurons. J Neurosci 1998;
TG, Moss SJ. Brain-Derived Neurotrophic
18(24):10231-40.
Factor Modulates Fast Synaptic Inhibition by
AA, Greengard P, Sihra TS. Synapsins As
Phosphorylation, Activity, and Cell-Surface
Stability. J Neurosci 2004; 24(2):522-30.
Neurotransmitter Release. Nat Neurosci 2000;
40. Bliss T, Collingridge G. A Synaptic Model of
Memory: Long-Term Potentiation in the
47. Carvalho AL, Caldeira MV, Santos SD, Duarte
Hippocampus. Nature 1993; 361(6407):31-9.
CB. Role of the Brain‐Derived Neurotrophic
41. Malenka R, Nicoll R. Long-Term Potentiation
Factor at Glutamatergic Synapses. Br J
a Decade of Progress. Science 1999;
Pharmacol 2008; 153(S1):S310-24.
285(5435):1870-4.
42. Koo JW, Mazei-Robison MS, Chaudhury D,
Neurotrophin-Induced
Juarez B, LaPlant Q, Ferguson D, et al. BDNF
Is a Negative Modulator of Morphine. Science
Hippocampus. Science 1995; 267(5204):1658-
2012; 338 (6103):124-8.
43. Knipper M, Penha BM, Blöchl A, Breer
49. Vaynman S, Ying Z, Yin D, Gomez-Pinilla F.
H, Thoenen H, Lindholm D. Positive Feedback
Exercise Differentially Regulates Synaptic
Between Acetylcholine and the Neurotrophins
Proteins Associated to the Function of BDNF.
Nerve Growth Factor and Brain‐Derived
Brain Res 2006;1070(1):124-30
Neurotrophic Factor in the Rat Hippocampus.
Eur J Neurosci 1994;6(4):668-71.
Neurotrophin-Evoked Depolarization Requires
44. Blöchl A, Sirrenberg C. Neurotrophins
the Sodium Channel NaV1. 9. Nature 2002;
Stimulate the Release of Dopamine from Rat
419(6908):687-93.
Mesencephalic Neurons via Trk and p75Lntr
51. Rose CR, Blum R, Pichler B, Lepier A, Kafitz
Receptors. J Biol Chem 1996; 271(35):21100-
Neurotrophin-Evoked
45. Li Y, Zhang Y, Lester H, Schuman
Signalling in Glia Cells. Nature 2003;
426(6962):74-78.
Source: http://cjns.gums.ac.ir/article-1-31-en.pdf
Incipient Fault Detection in 33/11kV Power Transformers by Using Combined Dissolved Gas Analysis Technique and Acoustic Partial Discharge Measurement and Validated Through Untanking Mohd Raffi Samsudin Ahmad Qisti Ramli Ahmad Berhanuddin Young Zaidey Yang Researcher, High Voltage Tenaga Nasional Bhd Universiti Tenaga Tenaga Nasional Bhd TNB Research Sdn Bhd
Wiri Wai Care Wonders! Students from Wiri Central School proudly sign W after completing work on the Puhinui stream. Learning goes beyond the classroom Drury School drain painting Wai Care Fieldtrip to Hunua Brendon with a longfin eel found during fish monitoring Drury School's Wai Care club recently painted up a Papakura Normal School's middle and senior


